In today’s post, we’re going to take a look at the fascinating world of ASCII tables. Now, you might be wondering, what is an ASCII table? Well, let me explain. ASCII, which stands for American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard that assigns unique numeric codes to represent each character in the English alphabet, numbers, and various symbols.
An ASCII table is a handy reference guide that lists all these characters along with their corresponding code numbers.
Let’s start with the basics. The ASCII table consists of 128 characters, which are represented by numbers ranging from 0 to 127. These characters include uppercase letters (A-Z), lowercase letters (a-z), digits (0-9), punctuation marks, symbols, and control characters. The table arranges these characters in a systematic manner, making it easy for computer programmers, researchers, and enthusiasts to look up specific characters and their corresponding codes.
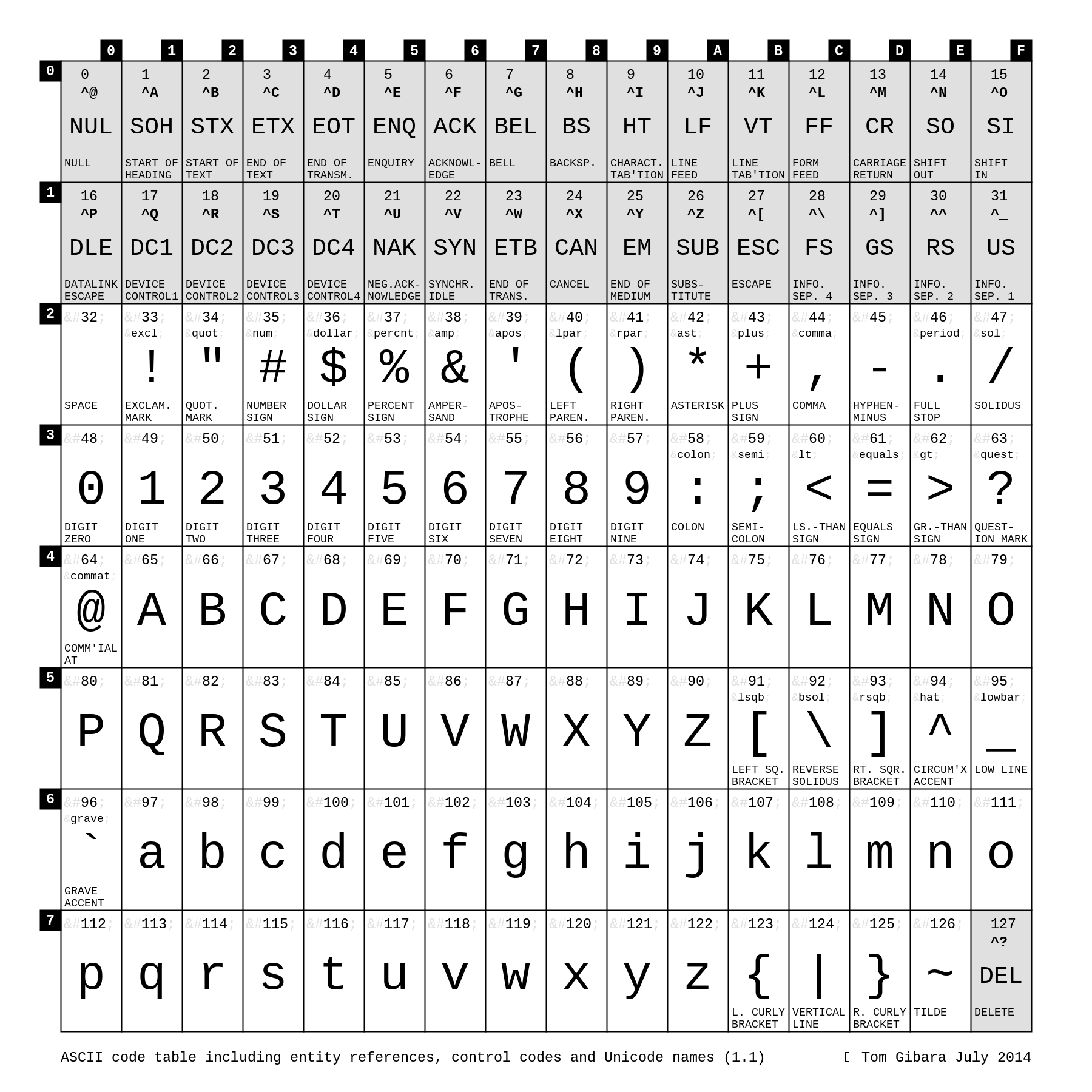 As you can see from the example above, the ASCII table provides a comprehensive overview of the characters and their associated codes. This visual representation makes it much easier to understand the relationships between characters and their numerical counterparts.
As you can see from the example above, the ASCII table provides a comprehensive overview of the characters and their associated codes. This visual representation makes it much easier to understand the relationships between characters and their numerical counterparts.
Now, you might be wondering why ASCII tables are relevant or useful in today’s digital age.
Well, despite the advancements in computer technology and the emergence of Unicode (a character encoding standard that supports multiple languages), ASCII still plays a crucial role in various programming languages, data conversion, and communication protocols. It serves as the foundation for many other character encoding schemes and is widely supported across different computing platforms.
 Whether you’re working with legacy systems, analyzing binary data, or even just trying to understand how computers interpret and display characters, having a good understanding of ASCII is incredibly valuable. ASCII tables provide a convenient way to access and interpret this information quickly.
Whether you’re working with legacy systems, analyzing binary data, or even just trying to understand how computers interpret and display characters, having a good understanding of ASCII is incredibly valuable. ASCII tables provide a convenient way to access and interpret this information quickly.
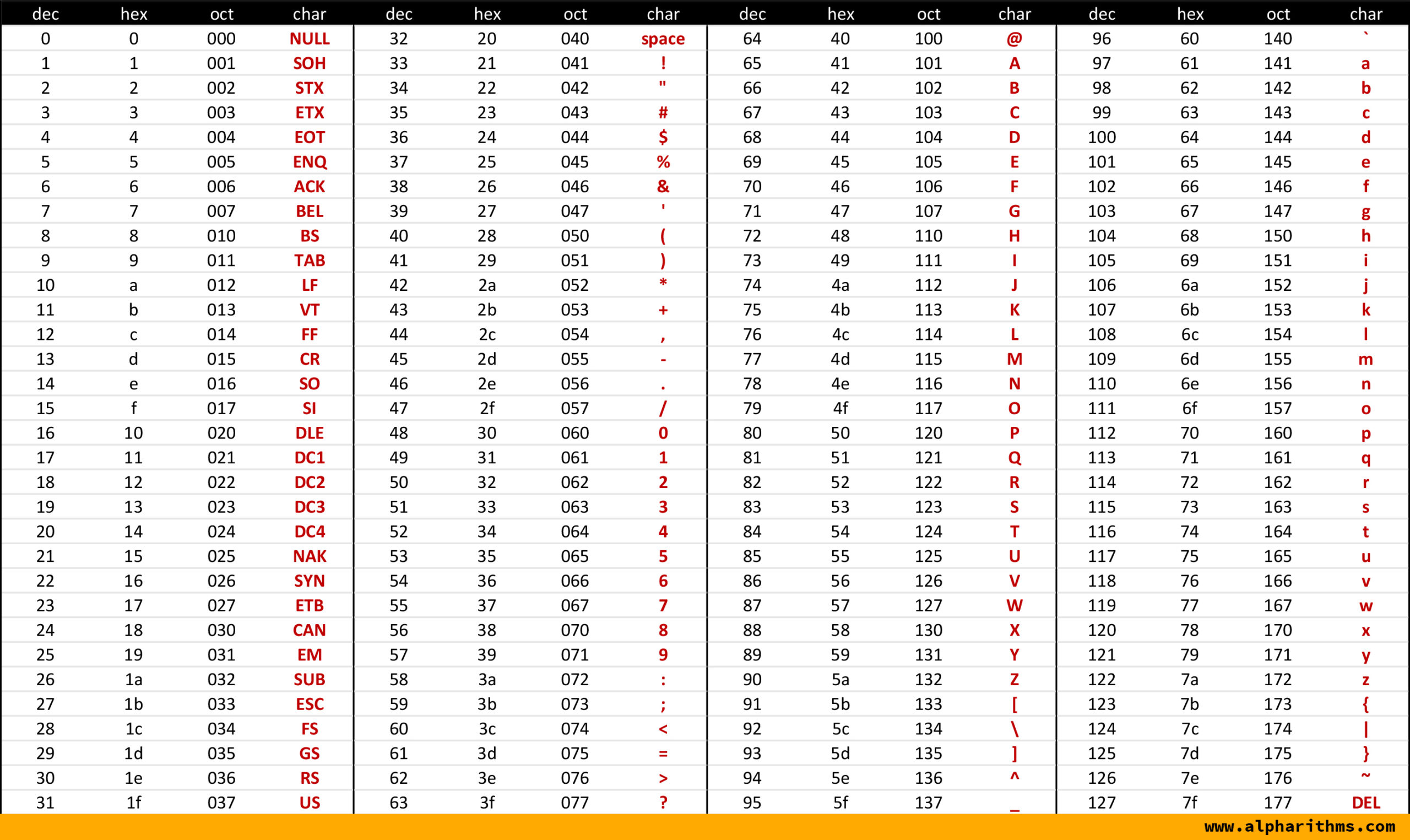 Now, let’s dive a bit deeper into the world of ASCII tables. Did you know that ASCII tables also include non-English characters? Although ASCII was primarily designed for the English language, certain extensions to the standard were developed to accommodate additional characters.
Now, let’s dive a bit deeper into the world of ASCII tables. Did you know that ASCII tables also include non-English characters? Although ASCII was primarily designed for the English language, certain extensions to the standard were developed to accommodate additional characters.
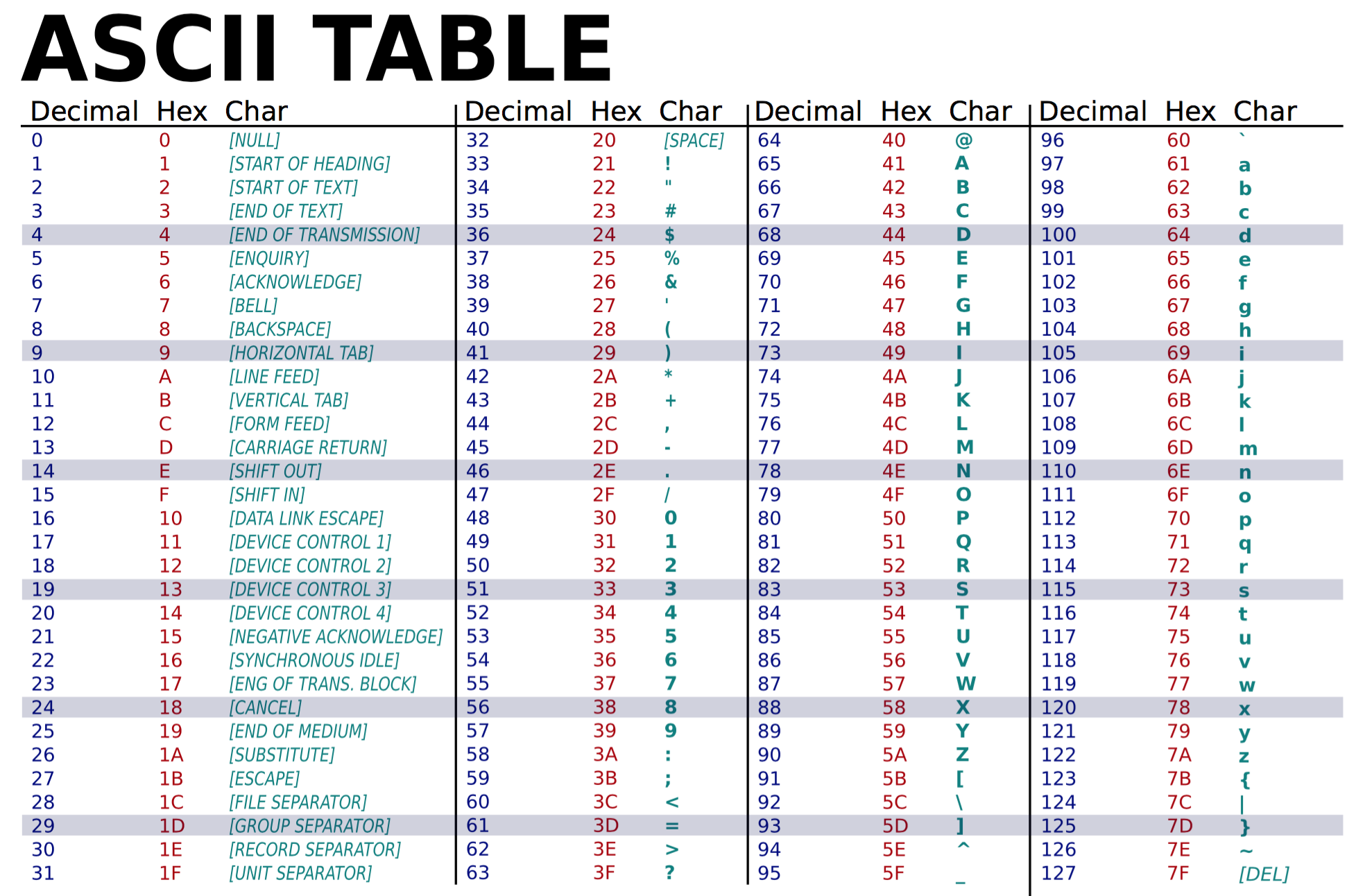 These extended ASCII tables include characters from other languages, such as French, German, Spanish, and many more. While these characters are not part of the original 7-bit ASCII standard, they are often used in specific regional contexts. Understanding these extended characters can be particularly useful for internationalization and localization purposes.
These extended ASCII tables include characters from other languages, such as French, German, Spanish, and many more. While these characters are not part of the original 7-bit ASCII standard, they are often used in specific regional contexts. Understanding these extended characters can be particularly useful for internationalization and localization purposes.
Now, let’s take a closer look at how to read an ASCII table.
Each row in the table represents a unique ASCII character and its associated code. The first column lists the decimal value of the code, the second column displays the hexadecimal value, and the third column showcases the actual character itself. For example, the character ‘A’ is represented by the decimal code 65, the hexadecimal code 41, and the actual character ‘A’.
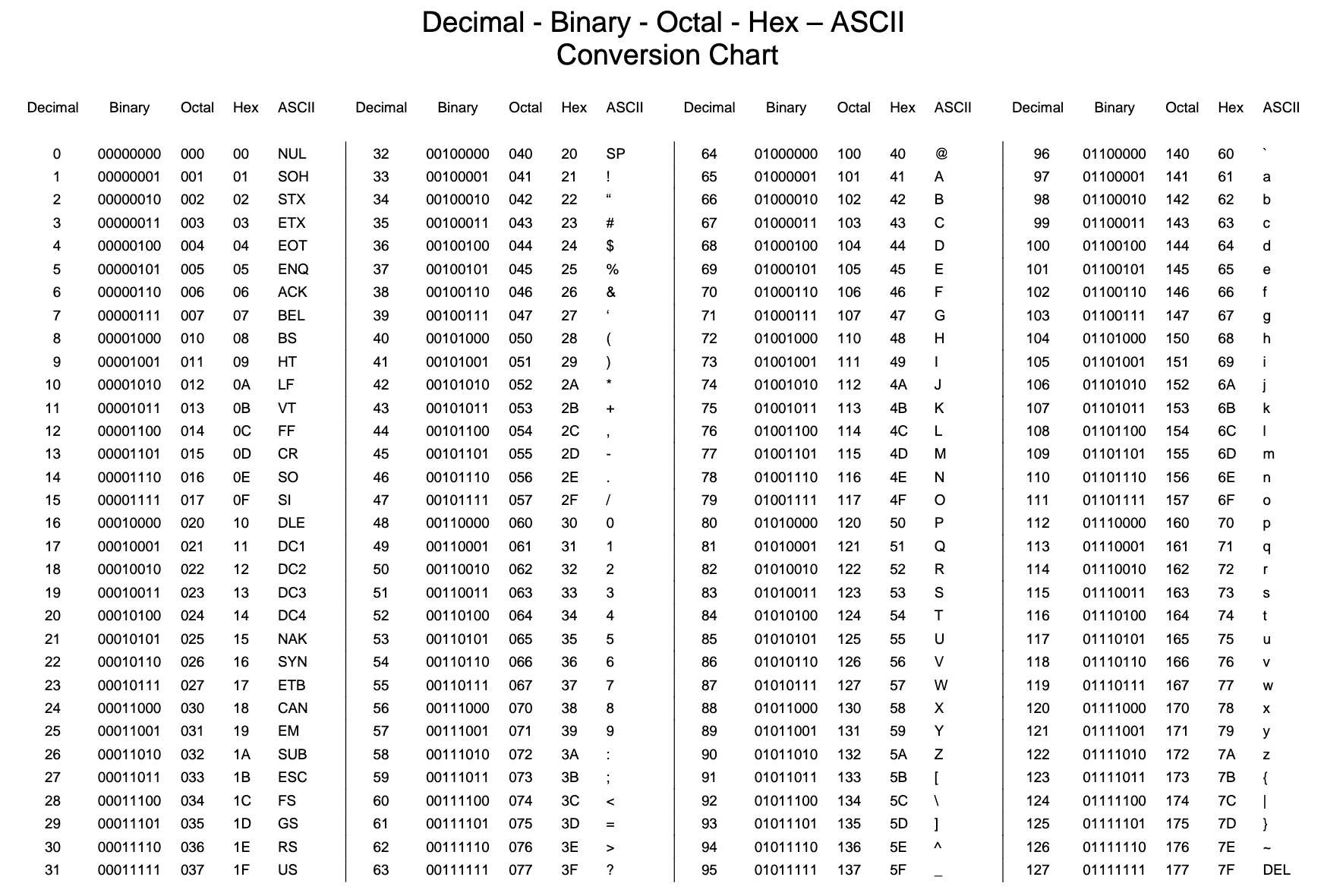 As you can see, ASCII tables provide a wealth of information for anyone working with characters in computing. Whether you’re a programmer, a student, or simply curious about the inner workings of computers, exploring ASCII tables can be an enlightening and educational experience.
As you can see, ASCII tables provide a wealth of information for anyone working with characters in computing. Whether you’re a programmer, a student, or simply curious about the inner workings of computers, exploring ASCII tables can be an enlightening and educational experience.

 So, the next time you come across an ASCII table, take a moment to appreciate its significance and all the knowledge it holds. From its humble beginnings to its enduring relevance in today’s modern computing landscape, ASCII tables continue to play a vital role in the world of technology.
So, the next time you come across an ASCII table, take a moment to appreciate its significance and all the knowledge it holds. From its humble beginnings to its enduring relevance in today’s modern computing landscape, ASCII tables continue to play a vital role in the world of technology.